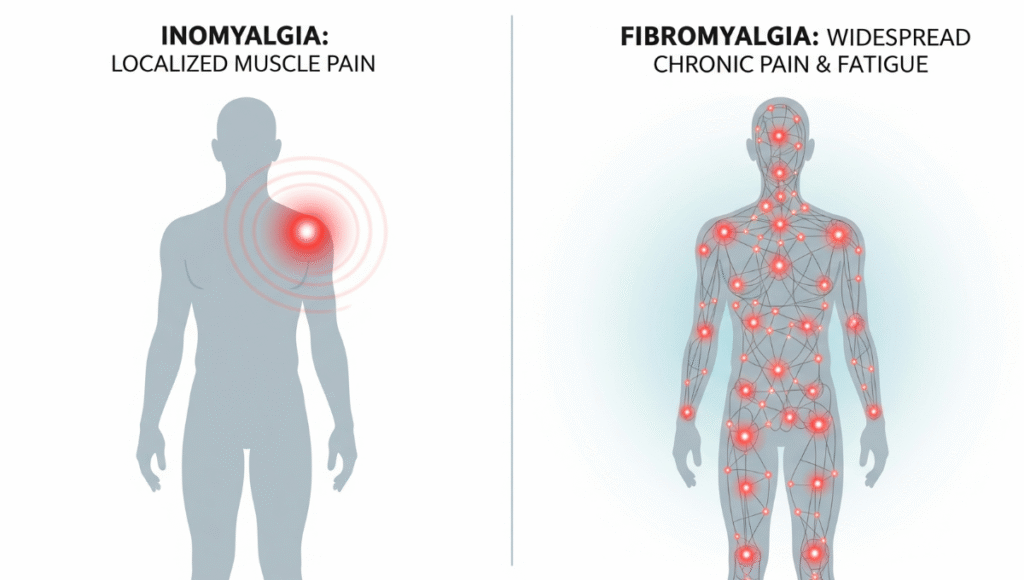
Chronic muscle pain and fatigue affect millions of people worldwide, but not all conditions causing these symptoms are the same. Inomyalgia and fibromyalgia are two disorders that often get confused due to overlapping signs, but understanding their differences is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment. This guide will help you distinguish between the two, explore symptoms, and highlight management strategies.
Discover more health advice and wellness guidance at MagazineVibe.co.uk
1. What Is Inomyalgia?
Inomyalgia is a condition characterized primarily by localized muscle pain. It often affects specific muscle groups and may be triggered by physical strain, stress, or minor injuries. Unlike systemic disorders, inomyalgia is usually confined to certain areas of the body.
Key Features of Inomyalgia:
-
Localized muscle tenderness
-
Muscle tightness accompanied by restricted movement in the affected areas.
-
Discomfort typically intensifies during movement and eases when at rest.
-
Rarely associated with systemic symptoms like fatigue or sleep disturbances
2. What Is Fibromyalgia?
Fibromyalgia is a long-term condition characterized by widespread muscle and joint pain, often accompanied by fatigue, disrupted sleep, and cognitive challenges. It affects multiple regions of the body and is considered a systemic condition. If not properly managed, fibromyalgia can greatly reduce a person’s overall quality of life.
Key Features of Fibromyalgia:
-
Widespread pain across multiple body regions
-
Fatigue and decreased energy levels
-
Sleep disturbances, including insomnia or restless sleep
-
Cognitive difficulties often referred to as “fibro fog”
-
Sensitivity to light, sound, or temperature changes
3. Comparing Symptoms: Inomyalgia vs. Fibromyalgia
| Symptom | Inomyalgia | Fibromyalgia |
|---|---|---|
| Pain Location | Localized to specific muscles | Widespread across body |
| Fatigue | Rare | Common and persistent |
| Sleep Disturbances | Rare | Frequent, may worsen symptoms |
| Cognitive Issues | Rare | Common (“fibro fog”) |
| Trigger Factors | Physical strain or minor injuries | Stress, hormonal changes, infections |
| Duration | Often short-term | Chronic, lasting months to years |
4. Causes and Risk Factors
Inomyalgia Causes:
-
Overuse of certain muscles
-
Minor injuries or strains
-
Poor posture or repetitive motions
Fibromyalgia Causes:
-
Exact cause unknown, but factors include:
-
Genetic predisposition
-
Abnormal pain processing in the nervous system
-
Stress, trauma, or infections triggering symptoms
-
Understanding these causes helps in developing appropriate management strategies.
5. Diagnosis: How to Tell the Difference
-
Inomyalgia Diagnosis: Typically involves a physical examination to identify tender muscle areas. Diagnostic imaging and laboratory tests can help exclude injuries or alternative medical conditions.
-
Fibromyalgia Diagnosis: Based on widespread pain lasting at least three months, along with associated symptoms like fatigue and cognitive issues. Blood tests help exclude other disorders.
Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial to avoid unnecessary treatments and target the right therapies.
6. Treatment and Management Options
For Inomyalgia:
-
Rest and avoiding overuse of affected muscles
-
Physical therapy to improve flexibility and strength
-
Pain relievers such as NSAIDs
-
Stress reduction and posture correction
For Fibromyalgia:
-
Medications to manage pain, fatigue, and sleep issues
-
Low-impact exercise such as yoga, swimming, or walking
-
Using cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) to manage stress and regulate mood.
-
Lifestyle changes including proper sleep hygiene and balanced diet
7. Lifestyle Tips for Both Conditions
-
Maintain a regular exercise routine appropriate to your condition
-
Prioritize sleep and relaxation techniques
-
Avoid activities that exacerbate pain or fatigue
-
Keep a symptom diary to identify triggers and monitor progress
Conclusion
While inomyalgia and fibromyalgia share similarities, the differences in pain distribution, associated symptoms, and chronicity make proper diagnosis essential. Inomyalgia typically involves localized muscle pain that improves with rest, whereas fibromyalgia is a chronic, systemic condition with widespread pain, fatigue, and cognitive difficulties.
Early recognition, appropriate medical care, and lifestyle management can greatly improve quality of life for individuals with either condition. For more health tips, wellness guides, and in-depth articles, visit MagazineVibe.co.uk.